Application Highlight: Infineon Connects Smart Lighting Systems
July 07, 2025
Sponsored Story

In smart buildings, smart homes, or any other IoT-enabled, connected, and (crucially) lit smart infrastructure, the lighting is often the first and best place to start. Smart lighting can result in greater energy efficiency at a lower cost than almost any other initiative. This ROI, delivered early and quickly, has made lighting a smart and strategic beginning to intelligent design for years.
Despite how long it’s been the best practice beginning point, connected and smart lighting is still a topic that draws attention and seems to always be driving momentum for smart buildings, and the last five years have seen a huge explosion of interest within the lighting industry.
Those designers in the lighting space who are digging in are looking for the key elements that will help realize energy savings, while also finding new applications and use cases that can go beyond lighting controls. They’re finding that competitive and innovative edge in the world of connectivity.
Application Use Cases
The oldest and first applications for smart lighting are always for energy savings. For this pillar use case, passive infrared (PIR) sensors have always been the key technology, but that’s changing. Engineers are finding that they need to leverage more sophisticated sensors like radar to overcome some of the weaknesses of PIR sensors. These weaknesses can include poor design, limited detection of micro-movements, and limited area coverage, among others. Having any of the faults can make a smart lighting system fail in its primary mission of being energy efficient, let alone finding new applications.
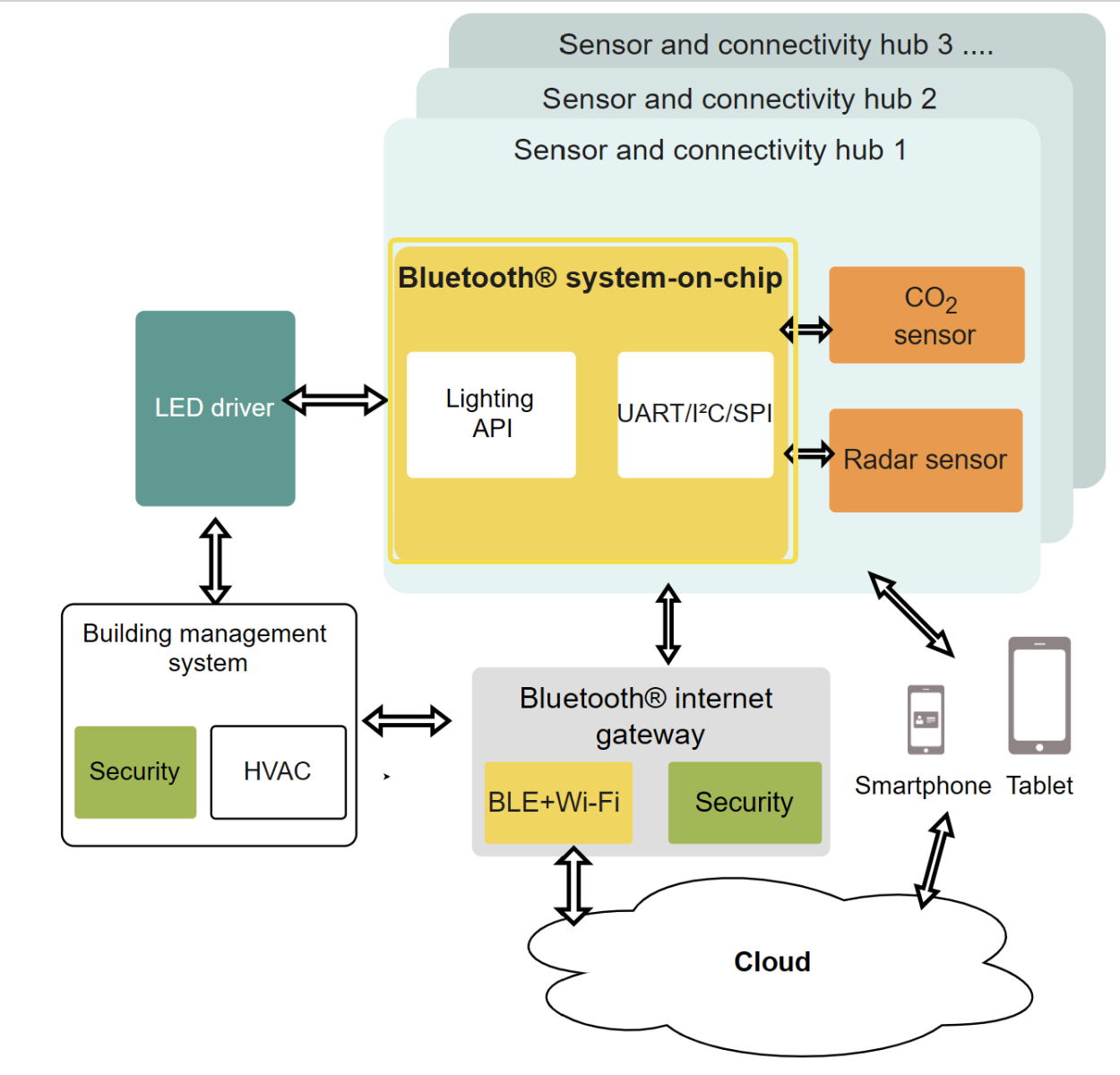
Radar sensors can now be integrated directly into luminaires, making for a sleeker and subtler design, in addition to enabling platform design for luminaires, since it eliminates the need for drilling holes, unlike PIR sensors. There are several more advanced use cases hitting the market now, too, now that radar is becoming readily available. Lighting is now capable of managing special controls through people counting and people tracking, thanks to radar technology integrations. Asset tracking and control also enter the purview of the intelligent lighting system, making possible the monitoring of meeting room use, desk occupancies, and even security tasks like recognizing unauthorized access to certain areas can be implemented, analyzed, and optimized.
In adding additional intelligence into the entire system that can handle the greater data loads for these advanced applications, connectivity is the critical element. Implementation of connectivity provides the following benefits:
- Cost reduction: Implementation of sensor hubs at select luminaires that can serve as a master for the other luminaires
- Simpler wiring and code: A central control unit with high computational power can be leveraged to serve as a master over all the luminaires
- A central control unit, potentially part of the Building Management System (BMS) or cloud, can address advanced use cases that go beyond pure lighting control
For achieving that indoors, building wide connectivity that enables every smart lighting use case, new and established, Bluetooth Mesh has become one of the key technologies in most leading systems implementations, thanks to its reliability, security, and near-universal interoperability. One major benefit to smart facility managers looking to install such a mesh is that Bluetooth devices that can be deployed as local control elements are ubiquitous and easy to obtain, while standardized, mature BT mesh stacks are easily available.
Infineon
Infineon AIROC Wi-Fi & Combos are designed to enable smart lighting connectivity, and they use production-ready, fully-certified Wi-Fi + Bluetooth combo modules based on both Linux and RTOS-based platforms. Many of the Wi-Fi + Bluetooth combos are supported on Infineon’s WICED Wi-Fi and ModusToolbox Software Development Kits (SDKs), which provide code examples, tools, and development support for easier and faster development.
Infineon’s ModusToolbox software and tools provide code examples and development support for Wi-Fi SoCs or adding Infineon’s secure and low-power PSoC MCUs and sensors to IoT applications. Infineon also supports customers through its global network of IoT partners using production-ready, fully-certified AIROC Wi-Fi & combo modules based on both Linux and RTOS-based platforms.
The AIROC portfolio is designed with integrated IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.4 in a single-chip solution to enable small-form-factor IoT designs like lighting units.
Combo, standalone Wi-Fi, and Wi-Fi SoCs with embedded MCU and on-chip networking capabilities are also offered in 1x1 SISO and 2x2 MIMO configurations, the company says. Wi-Fi and combo solutions can be coupled with external MCUs from Infineon and others for RTOS, along with Linux on application processors to implement a complete Wi-Fi + Bluetooth/Bluetooth Low Energy system. AIROC Wi-Fi SoCs include on-chip MCUs, memory, and the networking protocols required for customers to easily create their own cloud-connected applications.
Smart lighting is a perfect place to start in any smart building plan, but it’s also the best way to create a comprehensive, ubiquitous smart facility, thanks to Bluetooth Mesh and Wifi connectivity.
Additional Resources:
- Infineon AIROC: https://www.infineon.com/cms/en/product/wireless-connectivity/airoc-wi-fi-plus-bluetooth-combos/
- Product Page: https://www.infineon.com/cms/en/applications/smart-home-building/home-building-automation/connected-and-smart-lighting/?tab=~%27development_tools#!designsupport
- Infineon LED Lighting Brochure: https://www.infineon.com/dgdl/Infineon-General_Lighting_LED-ApplicationBrochure-v05_00-EN.pdf?fileId=db3a304327b897500127f76de0b2654b