Demonstrating Power-Efficient Multi-Model AI Inference on an Edge Platform Featuring AIMB-2210 and AMD Ryzen Embedded 8000
December 29, 2025
Blog

The Secret AI Trio to Make Devices Smarter
System designers increasingly look for platforms capable of handling multiple AI workloads with efficient power consumption and low latency. Recent developments in embedded processors now combine general-purpose compute, graphics acceleration, and dedicated neural processing capabilities into a single System-on-Chip.
This article provides a technical walk-through demonstrating multi-model AI inference performance on the AIMB-2210 Mini-ITX platform featuring the AMD Ryzen Embedded 8000 processor.
Why Multiple AI Engines at the Edge?
Many industrial AI workloads require running several inference pipelines concurrently at the edge. For example, performing object detection, feature extraction, segmentation, and face recognition in parallel.
In these environments, AI is no longer only operating and processing computing tasks from the cloud, such as chatbots or generative tools, but needs to move to edge devices, or devices on site that can respond quicker and more tactically, significantly shortening response times, enhancing privacy and security, and mitigating network instability by not relying on a cloud service or connection.
The CPU-GPU-NPU architecture offers a multifunctional, diverse approach to processing designed to serve edge environments, such as factory automation, smart robotics, smart retail, and intelligent transportation.
Software Environment
- New AMD Ryzen AI Software Suite: AI Development Made Easy
Our engineering team used AMD Ryzen™ AI Software, a suite of tools that enables trained models from mainstream AI frameworks (like PyTorch and TensorFlow) to be quickly deployed on local NPU/GPU hardware.
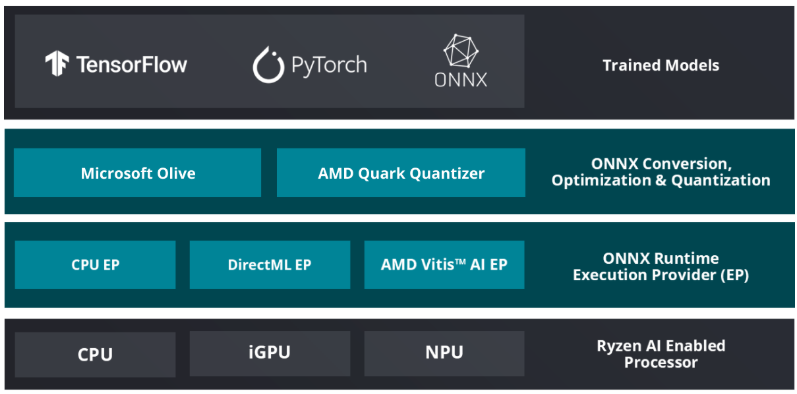
AMD also provides a curated model, named AI Model Zoo, to accelerate development. Engineers can experiment without deep AI compiler knowledge, making it suitable for embedded software teams transitioning into AI workloads.
Evaluation Objectives and Methods
- Objective: Validate whether the NPU can run multiple computer-vision models simultaneously and measure inference performance relative to CPU and iGPU execution.
- Platform: AIMB-2210 + AMD Ryzen Embedded 8000
- Development Tool: AMD Ryzen AI Software 1.2
Step 1: Preparation and Installation
Follow official guidelines to install the operating system, drivers, and AMD Ryzen AI Software.


Step 2: Deploy Multiple Models Simultaneously
Use AMD's provided multi-model sample to run five image AI models, namely MobileNet_v2, ResNet50, Retinaface, Segmentation, and Yolox, simultaneously on the NPU.
**Important: All steps are performed in Windows CMD.
Step 3: Results!
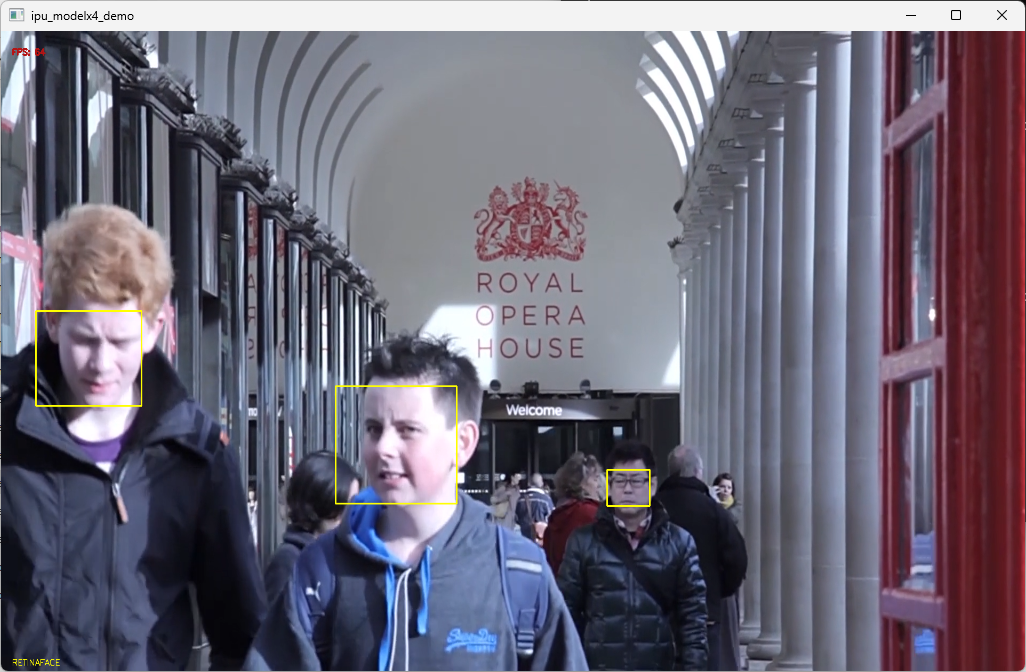
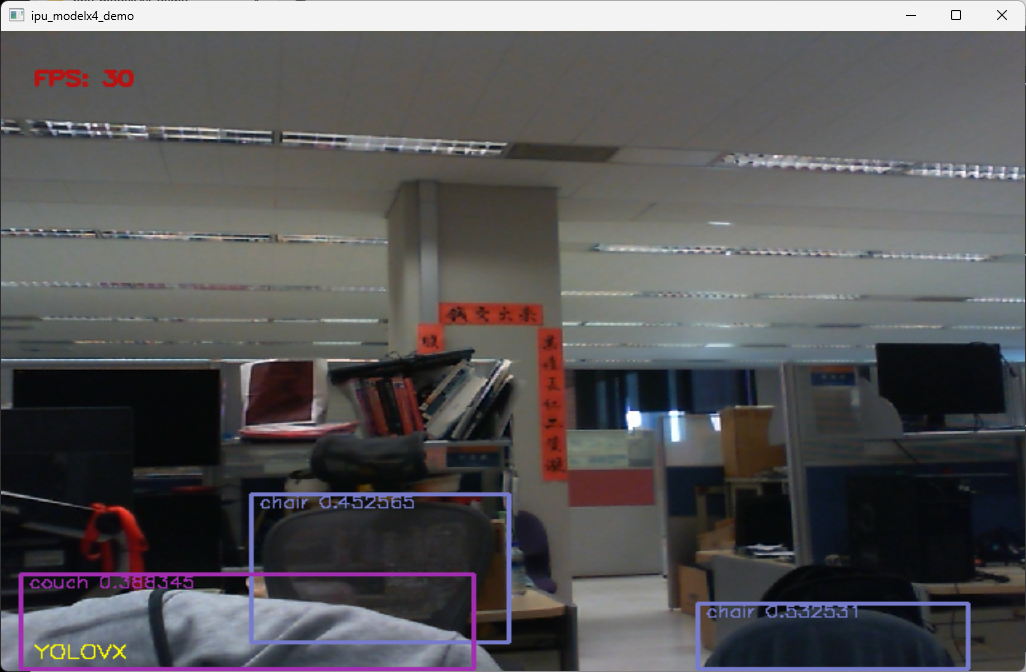
- Face Detection: Accurately identifies faces in images.

- Object Detection (Yolox): Quickly recognizes various objects.
Bonus: GPU DirectML Can Also Run AI
Explore the built-in RDNA 3 GPU of Ryzen 8000, utilizing Microsoft DirectML to accelerate models like YOLOv4.

NPU Performance Benchmark
Objective: Quantify the speed (throughput & latency) of NPU executing AI models.
Step 1: Testing Tools
Use AMD Ryzen AI Software's “performance_benchmark.py” to test ONNX format CNN models on CPU, iGPU, and NPU.
Step 2: Execution Process
Follow the GitHub guide for operation.
Step 3: Command Examples
- CPU: python performance_benchmark.py -m .\models\resnet50\resnet50_fp32.onnx -n 100 -e CPU
- iGPU: python performance_benchmark.py -m .\models\resnet50\resnet50_fp32.onnx -n 100 -e iGPU
- NPU: python performance_benchmark.py -m .\models\resnet50\resnet50_fp32.onnx -n 100 -e VitisAIEP
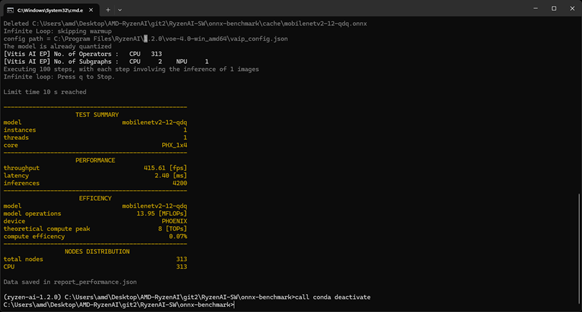
Benchmark Results (Mobilenet-v2)
The lightweight Mobilenet-v2 (quantized) model performs exceptionally well on the NPU, with FPS and latency data shown in the image.
Takeaways for Embedded System Engineers
Key technical observations from this evaluation include:
- Feasibility: AMD Ryzen Embedded 8000 can sustain multiple CV inference tasks simultaneously on an embedded form factor like Mini-ITX.
- Efficiency: NPU inference is fast and energy-efficient, especially suitable for edge devices requiring real-time response and long-term operation.
- Architecture flexibility: CPU, GPU, and NPU resources can be used independently or collaboratively, depending on workload distribution
Outlook
This evaluation assumes the AMD Ryzen Embedded 8000 processor is running on a Mini-ITX platform.
The same processor family is also available across multiple embedded form factors, including computer-on-modules (SOM-6873), Mini-ITX motherboards (AIMB-2210), small systems (AIR-410), fanless embedded systems (ARK-3535), and signage-oriented platforms (DS-054). These options allow engineers to select the appropriate platform architecture based on the thermal envelope, mechanical constraints, and application needs in areas such as industrial automation, robotics, retail automation, and smart city deployments.
Embedded x86 platforms now offer a viable path for running parallel edge AI workloads without relying solely on discrete accelerators. Engineers evaluating edge computing roadmaps can consider heterogeneous processor architectures as an option for compact, power-sensitive, and scalable AI deployments.