VPN Technologies Explained: SSL VPN vs. IPSec
August 26, 2025
Blog

With data breaches and cyber-attacks becoming a daily event across the globe, the question of secure communication cannot be overemphasized. Regardless of whether it is a business or an individual, it is imperative that the information that is transmitted through means such as the Internet is protected.
Introducing two of the greatest technologies of secure connections, namely SSL VPN and IPSec. But what differentiates these two, and why should you be interested?
What is an SSL VPN?
An SSL VPN also stands for Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network and is a network connection technology that provides secure remote access to an organization’s network and applications.
It refers to a VPN that connects by using the SSL/TLS protocol to develop a secure connection.
Here are some key points about SSL VPN:
SSL VPNs are typically web-based and provide two common types of connections: web connections and CIFS connections. In most cases, SSL VPN is established through a standard web browser, which makes it simple to access without requiring complex configurations.
Ease of use is its biggest advantage, as it generally does not require users to install additional software on their devices.
This type of VPN is also highly flexible, allowing secure access from nearly any internet-enabled device, whether it’s a computer, tablet, or smartphone.
Unlike traditional VPNs that give access to an organization’s entire network, SSL VPNs work at the application level, providing access only to specific programs.
How SSL VPN Works
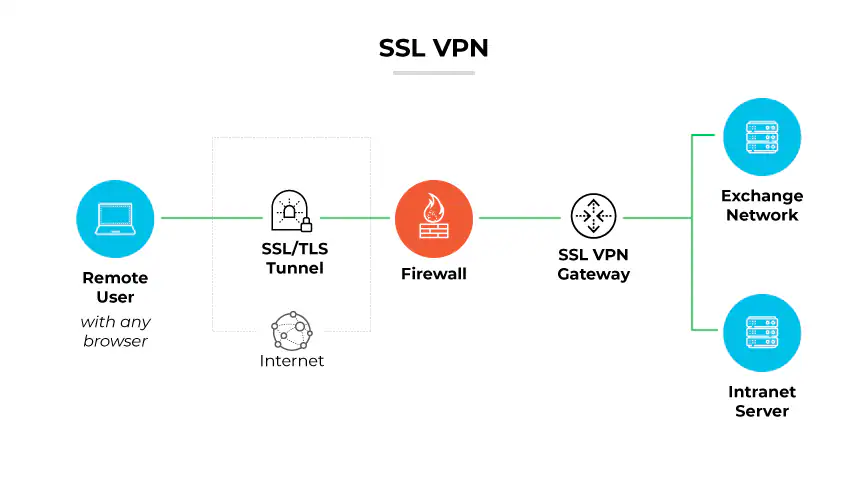
(Image: Source)
SSL VPN creates a secure tunnel for data to travel through.
Here's a simplified explanation of the process:
- The user connects to a website (often a company portal).
- The website and the user's device perform an SSL handshake.
- They agree on encryption keys.
- A secure connection is established.
- The user can now access authorized resources through this secure tunnel.
Advantages of SSL VPN
- Ease of Use: In most cases, SSL VPN doesn’t require special software. It can be accessed from any device with a web browser.
- Flexibility: Works well for remote access scenarios. It can be used on public computers or mobile devices.
- Granular Access Control: Administrators can control access to specific applications. Easier to manage user permissions.
- Lower Cost: Often cheaper to implement and maintain than IPSec. Requires less hardware and configuration.
- Better for Application-Level Access: Ideal for accessing web-based applications. Can provide a more seamless user experience.
Disadvantages of SSL VPN
- Limited Functionality: May not support all types of applications or protocols. Typically, it doesn't provide full network access.
- Performance: Can be slower than IPSec for large data transfers. May have higher latency due to encryption overhead.
- Security Concerns: Relies on the security of the web browser. Potentially vulnerable to certain web-based attacks.
- Complexity for Full Network Access: Requires additional configuration for non-web applications. May need client-side software for more comprehensive access.
What is IPSec?
IPSec stands for Internet Protocol Security. It's a suite of protocols designed to secure internet communication.
Here are some more details about IPSec:
In IPSec VPN, Network-layer security works at the IP layer of a network, which means it protects data as it moves between devices or systems. Unlike solutions that secure only specific applications, this method is comprehensive, as it can safeguard all traffic passing between two points, ensuring confidentiality and integrity throughout the process.
IPSec is also widely supported. Many operating systems and network devices have built-in IPSec compatibility, which makes it easier to implement it without any additional tools.
Its versatility allows it to be used in different scenarios, from connecting entire networks through site-to-site VPNs to providing secure connections for individual users via remote access VPNs.
How Does IPSec Work?
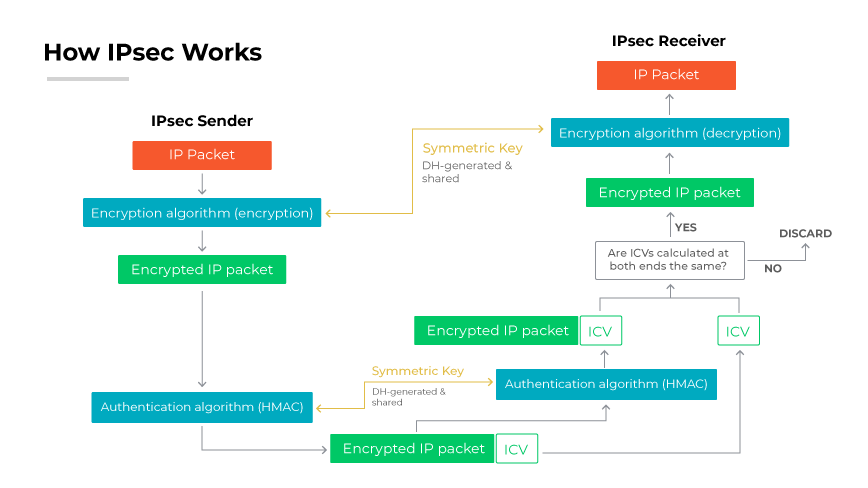
(Image: Source)
IPSec creates a secure tunnel at the network layer.
Here's a simplified explanation:
- Two pieces of equipment, for example, a computer and a server intended to pass data.
- It negotiates security parameters with the help of the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol.
- It is used by them when they agree on encryption and authentication methods.
- By utilizing this, it creates a secure channel between the devices.
- The communication that takes place between these devices is 100% encrypted, and the messages are also authenticated.
Advantages of IPSec
- Comprehensive Security: Secures all traffic between two points. Provides both encryption and authentication.
- Strong Security: Uses robust encryption algorithms. Less vulnerable to certain types of attacks.
- Transparency: Works with any IP-based application. Users don't need to change their workflow.
- Performance: It can be faster than SSL VPN for large data transfers. Lower latency for real-time applications.
- Ideal for Site-to-Site Connections: Excellent for connecting entire networks securely. Works well for branch offices or partner networks.
Disadvantages of IPSec
- Complexity: Can be more difficult to set up and manage. You will need specialized knowledge to configure properly.
- Less Flexible for Remote Access: Requires client software on user devices. It may not work well with public computers or some mobile devices.
- Potential Firewall Issues: Can be blocked by some firewalls. May require a special configuration to work in all network environments.
- Cost: Often more expensive to implement than SSL VPN. May require dedicated hardware or software licenses.
- Less Granular Access Control: Typically provides access to the entire network. It can be more challenging to restrict access to specific resources.
Key Differences Between SSL VPN and IPSec
|
Category |
SSL VPN |
IPSec |
|
Network Layer |
Operates at the application layer, often through a web browser. |
Operates at the network layer, securing all IP traffic. |
|
Ease of Use |
Easier for end-users, usually only needs a web browser. |
Requires client software and more configuration. |
|
Access Control |
Offers granular control over which applications users can access. |
Typically provides access to the entire network. |
|
Performance |
May have higher latency due to encryption overhead. |
Performs better for large data transfers and real-time applications. |
|
Flexibility |
More flexible for remote access from various devices. |
Better for site-to-site connections and full network access. |
|
Security Strength |
Highly secure when properly implemented. |
Often considered more robust due to its comprehensive approach. |
|
Cost |
Typically, less expensive to implement and maintain. |
May require more specialized hardware and expertise. |
|
Compatibility |
Works with almost any device that has a web browser. |
May have compatibility issues with some networks or devices. |
Choosing Between SSL VPN and IPSec
Therefore, the decision to use SSL VPN and IPSec is defined more by individual requirements.
Here are some scenarios to consider:
Choose SSL VPN:
For applications that you need to access remotely, and your users might be operating from different devices or even public computers to reach your site. In such cases, you want a solution that can be easily adopted by end-users, usually without requiring assistance from IT personnel.
At the same time, it should be an inexpensive remote access option while still allowing fine-grained control over how users interact with different resources on the network.
Choose IPSec:
You want to connect entire networks remotely through a site-to-site VPN and ensure the highest level of encryption for all traffic passing through the network.
When handling large volumes of data, time is critical, and essential that the solution works efficiently with a wide range of network protocols and various applications. This also means you should have the capability and the right tools to manage a more complex and intricate system effectively.
Conclusion
Internet Protocol and Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network are two of the most effective methods to secure communication in a network, with each benefit having its unique features.
VPN technology has become an important factor in the security of computer networks due to the changing nature of threats, therefore, the process of updating knowledge about VPN technologies, as well as the consistent use of updates and strict authentication.
Miles Brown is a marketing expert with 15+ years in business consulting, writing on cybersecurity, digital marketing tactics, and secure software development practices.